中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 211-226.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00066
• • 上一篇
周得龙1( ), 王永芳1,2,3(
), 王永芳1,2,3( ), 郭恩亮1,2, 红英1,2, 马浩文1, 慕全飞1, 王妍力1
), 郭恩亮1,2, 红英1,2, 马浩文1, 慕全飞1, 王妍力1
收稿日期:2025-02-28
修回日期:2025-05-31
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-08-18
通讯作者:
王永芳
作者简介:周得龙(1997—),男,甘肃景泰人,硕士研究生,主要从事生态环境遥感研究。E-mail: 2021385293@qq.com
基金资助:
Delong Zhou1( ), Yongfang Wang1,2,3(
), Yongfang Wang1,2,3( ), Enliang Guo1,2, Ying Hong1,2, Haowen Ma1, Quanfei Mu1, Yanli Wang1
), Enliang Guo1,2, Ying Hong1,2, Haowen Ma1, Quanfei Mu1, Yanli Wang1
Received:2025-02-28
Revised:2025-05-31
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
Yongfang Wang
摘要:
科尔沁沙地作为中国土地沙化严重的地区之一,其生境质量直接关系到区域生态环境和生态安全。运用集成价值评估工具模型(Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs,InVEST)的生境质量模块对科尔沁沙地1990—2022年生境质量进行评估,并通过动态度模型、Theil-Sen Median趋势分析法、Mann-Kendall检验、Hurst指数和地理探测器等,探讨科尔沁沙地生境质量时空演变特征及其影响因素。同时,耦合灰色多目标决策(Grey Multi-Objective Programming,GMOP)与斑块生成土地利用变化(Patch-generating Land Use Simulation,PLUS)模型,开展生态、自然、经济和综合发展情景下科尔沁沙地生境质量预估研究。结果表明:1990—2022年科尔沁沙地生境质量总体呈改善态势,且具备可持续性特征。空间上呈西高东低的分布格局,其中14.73%区域生境质量显著改善。地理探测器结果表明,植被因子是影响科尔沁沙地生境质量变化的主要因素,与地形、气候及人类活动等因子的交互作用对生境质量的空间异质性表现出更强的解释力。预测2035年研究区生境质量继续上升,在4种模拟情景中,生态保护情景下生境质量提升最为显著,低生境质量区域面积逐渐减少,一般等级和高等级生境质量面积有所增长。
中图分类号:
周得龙, 王永芳, 郭恩亮, 红英, 马浩文, 慕全飞, 王妍力. 科尔沁沙地生境质量演变与预测[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 211-226.
Delong Zhou, Yongfang Wang, Enliang Guo, Ying Hong, Haowen Ma, Quanfei Mu, Yanli Wang. Evolution and prediction of habitat quality in the Horqin Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(4): 211-226.
| 驱动因子/单位 | 空间分辨率 | 时间(年份) | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔/m | 30 m | 2000 | NASA官网(https://www.nasa.gov) |
| 坡度/m | |||
| 归一化植被指数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI)/(无量纲) | 1 km | 2000—2022 | NASA地球观测数据(https://earthdata.nasa.gov) |
| 净初级生产力(Net Primary Productivity,NPP)/(kg·m-2·a-1) | 1 km | 地理空间数据云(www.gis5g.com) | |
| 叶面积指数(Leaf Area Index,LAI)/(m2·m-2) | 500 m | NASA官网(https://modaps.modaps.eos⁃dis.nasa.gov/) | |
| 潜在蒸散量/mm | 0.042° | 1990—2022 | Terra Climate数据集(https://climate.northwestknowledge.net/) |
| 地表径流/mm | |||
| 土壤湿度/mm | |||
| 风速/(m·s-1) | |||
| 降水/mm | 1 km | 1990—2022 | 国家青藏高原数据中心(https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home) |
| 气温/℃ | |||
| 牲畜数量/头 | 0.083° | 2015 | 粮农组织牲畜系统(https://www.fao.org/livestock⁃systems/zh/) |
| GDP/万元 | 1 km | 2000—2020 | 地理空间数据云(www.gis5g.com) |
| 人口密度/(人·km-2) | WorldPop官网(https://hub.worldpop.org) |
表1 驱动因子数据说明
Table 1 Description of driving factor data
| 驱动因子/单位 | 空间分辨率 | 时间(年份) | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔/m | 30 m | 2000 | NASA官网(https://www.nasa.gov) |
| 坡度/m | |||
| 归一化植被指数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI)/(无量纲) | 1 km | 2000—2022 | NASA地球观测数据(https://earthdata.nasa.gov) |
| 净初级生产力(Net Primary Productivity,NPP)/(kg·m-2·a-1) | 1 km | 地理空间数据云(www.gis5g.com) | |
| 叶面积指数(Leaf Area Index,LAI)/(m2·m-2) | 500 m | NASA官网(https://modaps.modaps.eos⁃dis.nasa.gov/) | |
| 潜在蒸散量/mm | 0.042° | 1990—2022 | Terra Climate数据集(https://climate.northwestknowledge.net/) |
| 地表径流/mm | |||
| 土壤湿度/mm | |||
| 风速/(m·s-1) | |||
| 降水/mm | 1 km | 1990—2022 | 国家青藏高原数据中心(https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home) |
| 气温/℃ | |||
| 牲畜数量/头 | 0.083° | 2015 | 粮农组织牲畜系统(https://www.fao.org/livestock⁃systems/zh/) |
| GDP/万元 | 1 km | 2000—2020 | 地理空间数据云(www.gis5g.com) |
| 人口密度/(人·km-2) | WorldPop官网(https://hub.worldpop.org) |
| 胁迫因子 | 最大影响距离 | 权重 | 衰退相关性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 10 | 0.7 | 线性衰退 |
| 未利用地 | 5 | 0.6 | 指数衰退 |
| 建设用地 | 12 | 1 | 指数衰退 |
表2 胁迫因子权重设置
Table 2 Weight setting for stress factors
| 胁迫因子 | 最大影响距离 | 权重 | 衰退相关性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 10 | 0.7 | 线性衰退 |
| 未利用地 | 5 | 0.6 | 指数衰退 |
| 建设用地 | 12 | 1 | 指数衰退 |
| 土地利用类型 | 生境适宜性 | 耕地 | 未利用地 | 建设用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 1 |
| 林地 | 1 | 0.65 | 0.6 | 0.75 |
| 草地 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| 水域 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 建设用地 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 未利用地 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表3 生境敏感性设置
Table 3 Habitat sensitivity settings
| 土地利用类型 | 生境适宜性 | 耕地 | 未利用地 | 建设用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 1 |
| 林地 | 1 | 0.65 | 0.6 | 0.75 |
| 草地 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| 水域 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 建设用地 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 未利用地 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Z | 趋势变化类型 | |
|---|---|---|
| ≥0.0005 | >1.96 | 显著提升 |
| ≥0.0005 | -1.96 ~1.96 | 轻微提升 |
| -0.0005~0.0005 | -1.96~1.96 | 稳定不变 |
| <-0.0005 | -1.96~1.96 | 轻微退化 |
| <-0.0005 | <-1.96 | 显著退化 |
表4 Theil-Sen Median趋势变化类型判别标准
Table 4 Theil-Sen Median trend change type discrimination criteria
| Z | 趋势变化类型 | |
|---|---|---|
| ≥0.0005 | >1.96 | 显著提升 |
| ≥0.0005 | -1.96 ~1.96 | 轻微提升 |
| -0.0005~0.0005 | -1.96~1.96 | 稳定不变 |
| <-0.0005 | -1.96~1.96 | 轻微退化 |
| <-0.0005 | <-1.96 | 显著退化 |
| 判别标准 | 交互类型 |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 | |
| 单因子非线性减弱 | |
| 双因子增强 | |
| 独立 | |
| 非线性增强 |
表5 地理探测器判断标准及交互类型
Table 5 Types of geographical detector interactions and their discrimination criteria
| 判别标准 | 交互类型 |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 | |
| 单因子非线性减弱 | |
| 双因子增强 | |
| 独立 | |
| 非线性增强 |
表6 情景设置与土地利用预测条件
Table 6 Outlines the scenario settings and conditions for land use predictions
| 土地利用类型 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 水域 | 建设用地 | 未利用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经济价值系数/(万元·km-2) | 1.63 | 0.056 | 3.58 | 1.24 | 151.43 | 0 |
| 生态价值系数/(万元·km-2) | 0.98 | 4.90 | 3.00 | 31.26 | 0 | 4.42 |
表7 2035年科尔沁沙地土地利用类型生态价值与经济价值系数
Table 7 Coefficients of ecological and economic values of land use types in the Horqin Sandy Land by 2035
| 土地利用类型 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 水域 | 建设用地 | 未利用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经济价值系数/(万元·km-2) | 1.63 | 0.056 | 3.58 | 1.24 | 151.43 | 0 |
| 生态价值系数/(万元·km-2) | 0.98 | 4.90 | 3.00 | 31.26 | 0 | 4.42 |
| 约束类型 | 约束因素 | 约束表达式 | 约束条件解译 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总量 | 土地面积 | 各情景下土地利用总面积等于研究区面积 | ||
| 耕地红线 | 耕地面积 | 45538.38≤ | 由于科尔沁沙地耕地面积不断减少,以马尔科夫链预测的2035年耕地面积作为下限,以2022年耕地保有量作为上限 | |
| 林地 | 林地面积 | 8285.49≤ | 根据《全国重要生态系统保护和修复重大工程总体规划(2021—2035年)》,将全面加强科尔沁退化草原和已垦草原治理。因此,科尔沁沙地的林地会有所增加,将林地面积的下限设置为2022年林地面积,上限为马尔科夫链预测的2035年林地面积 | |
| 草地 | 草地面积 | 61152.03≤ | 随着科尔沁沙地实施了一系列生态保护和恢复政策,草原退化的趋势有所减缓。以马尔科夫链预测的2035年草原面积为上限,下限为2022年草地面积 | |
| 水域 | 水域面积 | 211.32≤ | 基于《内蒙古自治区“十四五”生态环境保护规划》,以西辽河流域为重点,逐步恢复水域生态功能。因此,以马尔科夫链预测的2035年水域面积作为上限,以2022年的水域面积作为下限 | |
| 建设用地 | 建设用地面积 | 3613.32≤ | 根据1990—2022年土地利用用地面积统计结果,科尔沁沙地建设用地面积不断增长。所以,以2022年建设用地面积为下限,以马尔科夫链预测的2035年建设用地面积为上限 | |
| 未利用地 | 未利用地面积 | 3357.63≤ | 科尔沁沙地1990—2022年未利用土地面积不断减少,因此上限为2022年未利用地面积,以马尔科夫链预测的2035的未利用地作为下限 | |
| 农用地 | 耕、林、草地面积 | 农业用地面积保持动态均衡,且不低于现状面积 | ||
| 生态多样性 | 林、草、水域面积 | 各优化情景下生态多样性总面积不低于现状面积 | ||
表8 科尔沁沙地土地预测约束条件
Table 8 Forecast constraints on land use in the Horqin Sandy Land
| 约束类型 | 约束因素 | 约束表达式 | 约束条件解译 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总量 | 土地面积 | 各情景下土地利用总面积等于研究区面积 | ||
| 耕地红线 | 耕地面积 | 45538.38≤ | 由于科尔沁沙地耕地面积不断减少,以马尔科夫链预测的2035年耕地面积作为下限,以2022年耕地保有量作为上限 | |
| 林地 | 林地面积 | 8285.49≤ | 根据《全国重要生态系统保护和修复重大工程总体规划(2021—2035年)》,将全面加强科尔沁退化草原和已垦草原治理。因此,科尔沁沙地的林地会有所增加,将林地面积的下限设置为2022年林地面积,上限为马尔科夫链预测的2035年林地面积 | |
| 草地 | 草地面积 | 61152.03≤ | 随着科尔沁沙地实施了一系列生态保护和恢复政策,草原退化的趋势有所减缓。以马尔科夫链预测的2035年草原面积为上限,下限为2022年草地面积 | |
| 水域 | 水域面积 | 211.32≤ | 基于《内蒙古自治区“十四五”生态环境保护规划》,以西辽河流域为重点,逐步恢复水域生态功能。因此,以马尔科夫链预测的2035年水域面积作为上限,以2022年的水域面积作为下限 | |
| 建设用地 | 建设用地面积 | 3613.32≤ | 根据1990—2022年土地利用用地面积统计结果,科尔沁沙地建设用地面积不断增长。所以,以2022年建设用地面积为下限,以马尔科夫链预测的2035年建设用地面积为上限 | |
| 未利用地 | 未利用地面积 | 3357.63≤ | 科尔沁沙地1990—2022年未利用土地面积不断减少,因此上限为2022年未利用地面积,以马尔科夫链预测的2035的未利用地作为下限 | |
| 农用地 | 耕、林、草地面积 | 农业用地面积保持动态均衡,且不低于现状面积 | ||
| 生态多样性 | 林、草、水域面积 | 各优化情景下生态多样性总面积不低于现状面积 | ||
| 生境质量等级 | 1990—2000年 | 2001—2011年 | 2012—2022年 | 1990—2022年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | |
| 低 | 71.44 | 0.09 | -251.62 | -0.33 | -105.06 | -0.15 | -904.79 | -1.29 |
| 较低 | -5 554.58 | -6.44 | 184.54 | 0.22 | 4 161.76 | 3.04 | -962.47 | -0.70 |
| 一般 | 684.49 | 0.18 | -941.83 | -0.26 | -1 652.36 | -0.48 | -3 566.45 | -1.04 |
| 较高 | 963.76 | 0.73 | -714.8 | -0.57 | 69.31 | 0.06 | 360.37 | 0.29 |
| 高 | 3 833.71 | 0.56 | 1 725.02 | 0.24 | -2 578.91 | -0.37 | 4 969.5 | 0.71 |
表9 1990—2022年各等级生境质量面积变化及动态度
Table 9 Changes in habitat quality area and dynamics by grade from 1990 to 2022
| 生境质量等级 | 1990—2000年 | 2001—2011年 | 2012—2022年 | 1990—2022年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km2 | 动态度/% | |
| 低 | 71.44 | 0.09 | -251.62 | -0.33 | -105.06 | -0.15 | -904.79 | -1.29 |
| 较低 | -5 554.58 | -6.44 | 184.54 | 0.22 | 4 161.76 | 3.04 | -962.47 | -0.70 |
| 一般 | 684.49 | 0.18 | -941.83 | -0.26 | -1 652.36 | -0.48 | -3 566.45 | -1.04 |
| 较高 | 963.76 | 0.73 | -714.8 | -0.57 | 69.31 | 0.06 | 360.37 | 0.29 |
| 高 | 3 833.71 | 0.56 | 1 725.02 | 0.24 | -2 578.91 | -0.37 | 4 969.5 | 0.71 |
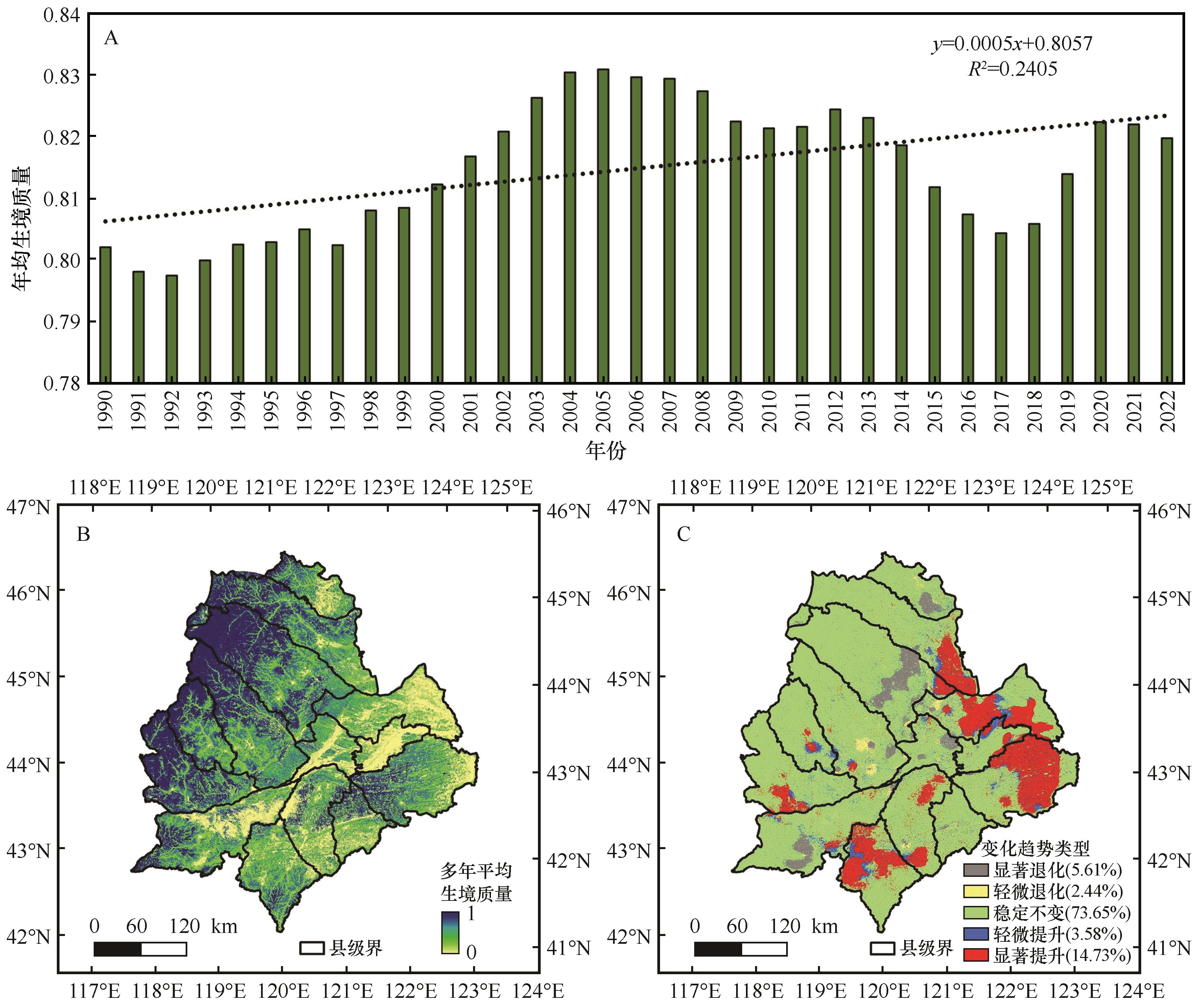
图3 科尔沁沙地1990—2022年生境质量时空演变特征注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号为GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.3 Spatiotemporal evolution of habitat quality in the Horqin Sandy Land from 1990 to 2022
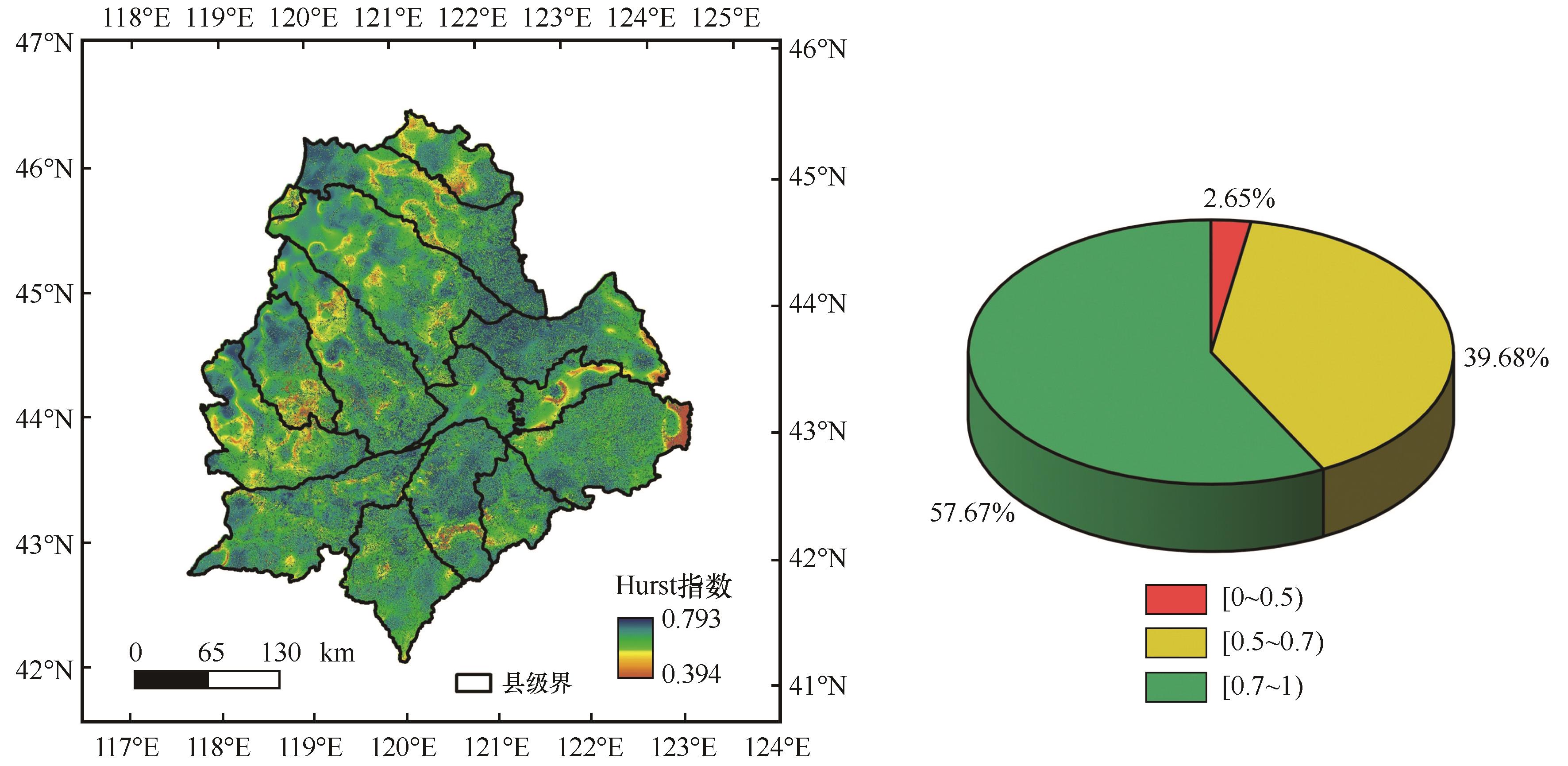
图4 科尔沁沙地1990—2022年Hurst指数空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号为GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.4 Spatial Distribution of the Hurst Index in the Horqin Sandy Land from 1990 to 2022
| 土地利用类型 | 2022年/km² | 2035年/km² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然发展情景 | 生态优先情景 | 经济优先情景 | 综合发展情景 | ||
| 耕地 | 48 542.94 | 49 426.29 | 46 261.91 | 46 556.50 | 46 191.57 |
| 林地 | 8 285.49 | 8 921.07 | 8 647.25 | 8 285.48 | 8 604.75 |
| 草地 | 61 152.03 | 59 123.7 | 62 405.78 | 62 405.72 | 61 739.07 |
| 水域 | 361.98 | 173.16 | 362.04 | 211.31 | 361.79 |
建设用地 未利用地 | 3 613.32 3 357.63 | 4 347.18 3 319.56 | 3 613.38 4 017.52 | 4 491.26 3 357.62 | 4 455.25 3 954.70 |
表10 科尔沁沙地不同情景下土地利用面积
Table 10 Land use area of Horqin Sandy Land under different scenarios
| 土地利用类型 | 2022年/km² | 2035年/km² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然发展情景 | 生态优先情景 | 经济优先情景 | 综合发展情景 | ||
| 耕地 | 48 542.94 | 49 426.29 | 46 261.91 | 46 556.50 | 46 191.57 |
| 林地 | 8 285.49 | 8 921.07 | 8 647.25 | 8 285.48 | 8 604.75 |
| 草地 | 61 152.03 | 59 123.7 | 62 405.78 | 62 405.72 | 61 739.07 |
| 水域 | 361.98 | 173.16 | 362.04 | 211.31 | 361.79 |
建设用地 未利用地 | 3 613.32 3 357.63 | 4 347.18 3 319.56 | 3 613.38 4 017.52 | 4 491.26 3 357.62 | 4 455.25 3 954.70 |
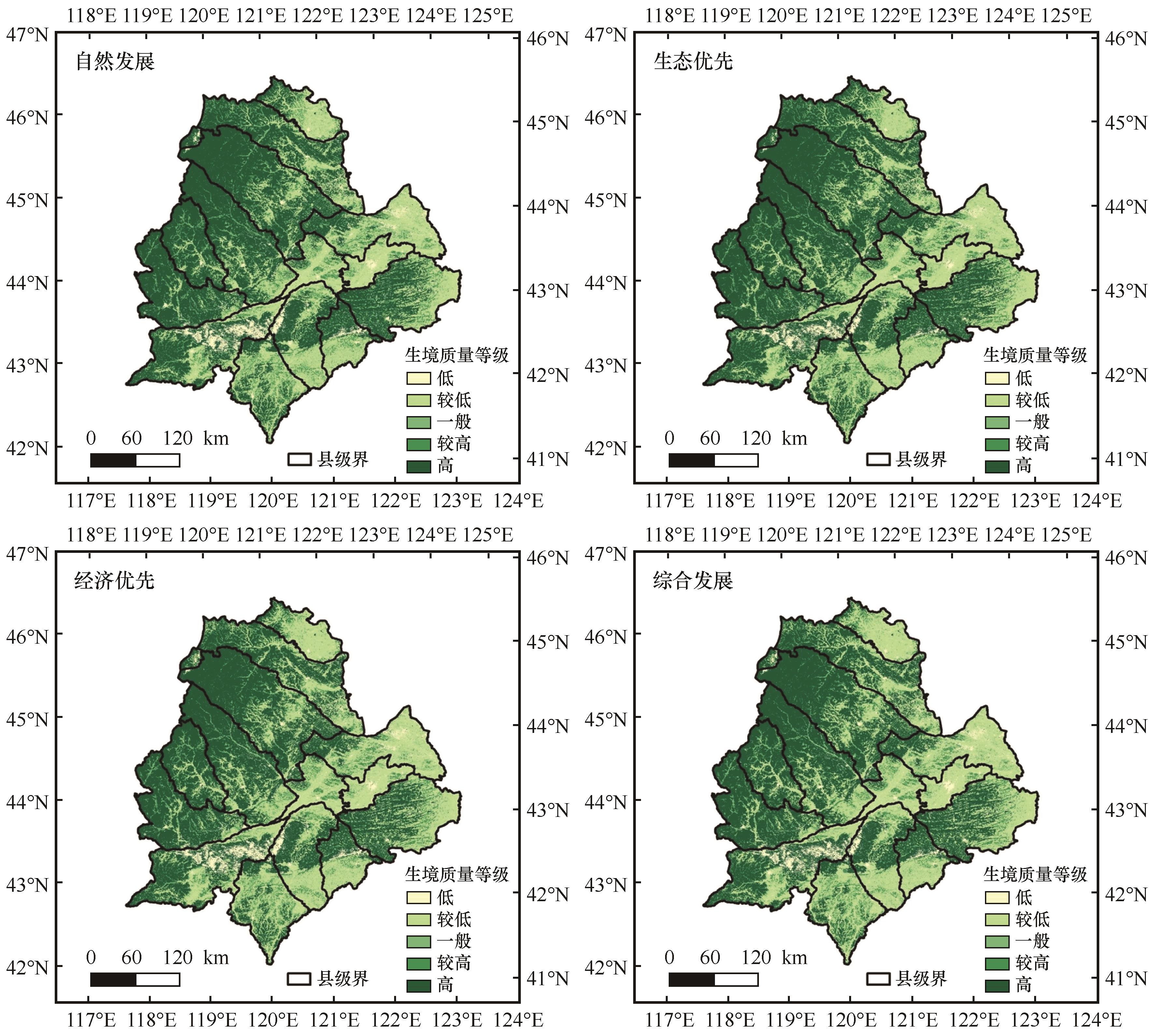
图7 科尔沁沙地2035年不同情景下生境质量预测空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号为GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.7 Spatial Distribution of Habitat Predictions in the Horqin Sandy Land Under Different Scenarios for 2035
| 生境质量等级 | 2022年/km² | 2035年/km² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然发展情景 | 生态优先情景 | 经济优先情景 | 综合发展情景 | ||
| 低 | 7 525.71 | 6 237.27 | 4 997.97 | 7 045.56 | 7 039.35 |
| 较低 | 39 831.3 | 38 109.33 | 39 229.02 | 42 789.87 | 44 056.71 |
| 一般 | 8 530.65 | 9 477.63 | 9 779.04 | 8 418.42 | 8 401.59 |
| 较高 | 7 078.32 | 6 864.48 | 6 654.51 | 6 894.81 | 7 075.89 |
| 高 | 62 344.98 | 64 622.25 | 64 650.42 | 58 918.5 | 59 981.22 |
表11 科尔沁沙地不同情景下生境质量面积
Table 11 Habitat quality area under different scenarios in the Horqin Sandy Land
| 生境质量等级 | 2022年/km² | 2035年/km² | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然发展情景 | 生态优先情景 | 经济优先情景 | 综合发展情景 | ||
| 低 | 7 525.71 | 6 237.27 | 4 997.97 | 7 045.56 | 7 039.35 |
| 较低 | 39 831.3 | 38 109.33 | 39 229.02 | 42 789.87 | 44 056.71 |
| 一般 | 8 530.65 | 9 477.63 | 9 779.04 | 8 418.42 | 8 401.59 |
| 较高 | 7 078.32 | 6 864.48 | 6 654.51 | 6 894.81 | 7 075.89 |
| 高 | 62 344.98 | 64 622.25 | 64 650.42 | 58 918.5 | 59 981.22 |
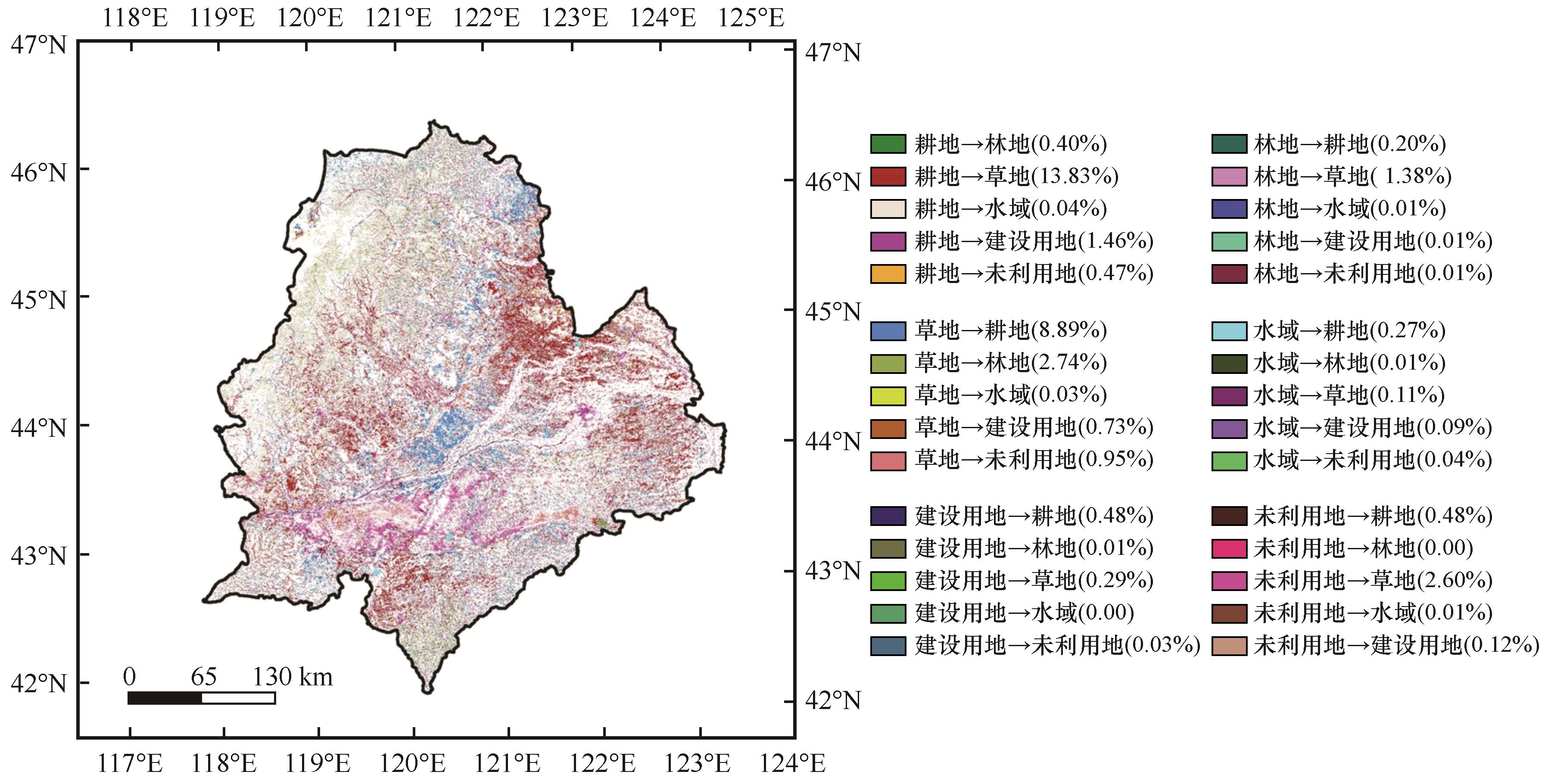
图9 科尔沁1990—2022年土地利用转移空间特征注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号为GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.9 Spatial changes in land use transition characteristics in Horqin (1990-2022)
| [1] | 胡云锋,张云芝,韩月琪.2000-2015年中国荒漠化土地识别和监测[J].干旱区地理,2018,41(6):1321-1332. |
| [2] | Reynolds J F, Smith D M S, Lambin E F,et al.Global desertification:building a science for dryland development[J].Science,2007,316(5826):847-851. |
| [3] | 张铜会,丛安琪,连杰,等.从科尔沁草原到科尔沁沙地的思考[J].应用生态学报,2024,35(1):25-30. |
| [4] | 李玉强,王旭洋,郑成卓,等.科尔沁沙地防沙治沙实践与生态可持续修复浅议[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(4):302-314. |
| [5] | 王康富,蒋瑾,张维静.京通铁路两侧防护体系的建立及其生态效益的研究:以奈曼地段为例[J].中国沙漠,1989,9(3):4-15. |
| [6] | 张晓明.三北防护林工程建设成效及发展对策[J].防护林科技,2020(2):52-54. |
| [7] | 刘峰,杨光,韩雪莹,等.科尔沁沙地土地利用时空演变及空间自相关分析:以奈曼旗为例[J].西北林学院学报,2020,35(4):148-157. |
| [8] | 王涛,宋翔,颜长珍,等.近35 a来中国北方土地沙漠化趋势的遥感分析[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(6):1351-1356. |
| [9] | 张寒冰,高阳,崔艳智.基于风沙防治的典型农牧交错区土地利用多情景模拟[J].环境科学研究,2019,32(6):1081-1089. |
| [10] | 张文昭.科尔沁、浑善达克两大沙地歼灭战稳步推进[J].国土绿化,2024(2):17-18. |
| [11] | 邵国媚,乔琴,张文婷,等.科尔沁草原生态功能区防风固沙功能时空变化及驱动因素分析[J].环境科学研究,2025,38(1):139-150. |
| [12] | 叶博文,孙标,赵云靓,等.2000-2022年内蒙古生境质量时空演变及驱动力分析[J].环境科学,2025,46(7):4473-4484. |
| [13] | Ma R, Lü Y, Fu B,et al.A modified habitat quality model to incorporate the effects of ecological restoration[J].Environmental Research Letters,2022,17(10):104029. |
| [14] | 印家旺,阿拉木萨,苏宇航,等.科尔沁沙地不同土地利用类型土壤入渗特征比较研究[J].水土保持通报,2022,42(4):90-98. |
| [15] | 杨志鹏,许嘉巍,冯兴华,等.基于InVEST模型的东北地区土地利用变化对生境的影响研究[J].生态科学,2018,37(6):139-147. |
| [16] | Yang J, Huang X.The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019[J].Earth System Science Data,2021,13(8):3907-3925. |
| [17] | Wang M, Guan Q.Prediction of potential suitable areas for Broussonetia papyrifera in China using the MaxEnt model and CIMP6 data[J].Journal of Plant Ecology,2023,16(4):rtad006. |
| [18] | Boumans R, Costanza R, Farley J,et al.Modeling the dynamics of the integrated earth system and the value of global ecosystem services using the GUMBO model[J].Ecological Economics,2002,41(3):529-560. |
| [19] | 高周冰,王晓瑞,隋雪艳,等.基于FLUS和InVEST模型的南京市生境质量多情景预测[J].农业资源与环境学报,2022,39(5):1001-1013. |
| [20] | 王成武,罗俊杰,唐鸿湖.基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J].生态环境学报,2023,32(2):215-225. |
| [21] | Wei Q, Abudureheman M, Halike A,et al.Temporal and spatial variation analysis of habitat quality on the PLUS-InVEST model for Ebinur Lake Basin,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2022,145:109632. |
| [22] | Jiang W, Deng Y, Tang Z,et al.Modelling the potential impacts of urban ecosystem changes on carbon storage under different scenarios by linking the CLUE-S and the InVEST models[J].Ecological Modelling,2017,345:30-40. |
| [23] | 周豹,赵俊三,陈国平,等.多情景模拟下滇东南喀斯特地区生态系统服务评估与网络优化[J].环境科学,2025,46(7):4615-4627. |
| [24] | 王军,严有龙,王金满,等.闽江流域生境质量时空演变特征与预测研究[J].生态学报,2021,41(14):5837-5848. |
| [25] | 顾汉龙,马天骏,钱凤魁,等.基于CLUE-S模型县域土地利用情景模拟与碳排放效应分析[J].农业工程学报,2022,38(9):288-296. |
| [26] | Zhang Y, Yu P, Tian Y,et al.Exploring the impact of integrated spatial function zones on land use dynamics and ecosystem services trade-offs based on a future land use simulation (FLUS) model[J].Ecological Indicators,2023,150:110246. |
| [27] | 胡碧松,张涵玥.基于CA-Markov模型的鄱阳湖区土地利用变化模拟研究[J].长江流域资源与环境,2018,27(6):1207-1219. |
| [28] | 智菲,周振宏,赵铭,等.基于PLUS和InVEST模型的合肥市生态系统碳储量时空演变特征[J].水土保持学报,2024,38(2):205-215. |
| [29] | 黄韬,刘素红.基于PLUS-InVEST模型的福建省土地利用变化与碳储量评估[J].水土保持学报,2024,38(2):246-257. |
| [30] | Liu X, Liu Y, Wang Y,et al.Evaluating potential impacts of land use changes on water supply-demand under multiple development scenarios in a dryland region[J].Journal of Hydrology,2022,610:127811. |
| [31] | Wang R, Zhao J, Chen G,et al.Coupling PLUS-InVEST model for ecosystem service research in Yunnan Province,China[J].Sustainability,2022,15(1):271. |
| [32] | 陈清飞,陈安强,叶远行,等.滇池流域土地利用变化对地下水水质的影响[J].中国环境科学,2023,43(1):301-310. |
| [33] | 张波,潘佩佩,王新云,等.基于GMOP-PLUS耦合模型的京津冀土地利用变化多情景模拟及功能关系分析[J].地理与地理信息科学,2023,39(5):8-16. |
| [34] | 胡波洋,张蓬涛,白宁,等.基于CLUE-S和GMOP模型的青龙满族自治县土地利用情景模拟[J].中国农业资源与区划,2020,41(7):173-182. |
| [35] | 马瑞,范燕敏,武红旗,等.耦合GMOP与PLUS模型的干旱区土地利用格局模拟[J].农业资源与环境学报,2023,40(1):143-153. |
| [36] | 许静,刘慧.甘肃省生态系统服务权衡协同关系评估与预测[J].中国环境科学,2024,44(4):1863-1874. |
| [37] | 中共中央,国务院.关于全面推进美丽中国建设的意见[N].人民日报,2024-01-12(1). |
| [38] | 苏立娟,李喜仓,邓晓东.1951-2005年内蒙古东部气候变化特征分析[J].气象与环境学报,2008,24(5):25-28. |
| [39] | 王妍力,王永芳,郭恩亮,等.科尔沁沙地生态安全格局时空演变规律研究[J].地理科学,2025,45(6):1341-1354. |
| [40] | Xue C, Chen X, Xue L,et al.Modeling the spatially heterogeneous relationships between trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services and potential drivers considering geographic scale in Bairin Left Banner,China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2023,855:158834. |
| [41] | 陈实,金云翔,黄银兰.长三角中心区生境质量时空变化及其影响机制[J].生态学杂志,2023,42(5):1175-1185. |
| [42] | 胡丰,张艳,郭宇,等.基于PLUS和InVEST模型的渭河流域土地利用与生境质量时空变化及预测[J].干旱区地理,2022,45(4):1125-1136. |
| [43] | Wang J F, Hu Y.Environmental health risk detection with GeogDetector[J].Environmental Modelling and Software,2012,33:114-115. |
| [44] | Yan X, Li J, Shao Y,et al.Driving forces of grassland vegetation changes in Chen Barag Banner,Inner Mongolia[J].GIScience & Remote Sensing,2020,57(6):753-769. |
| [45] | Wang F, Shao W, Yu H,et al.Re-evaluation of the power of the Mann-Kendall test for detecting monotonic trends in hydrometeorological time series[J].Frontiers in Earth Science,2020,8:14. |
| [46] | Zhang H, Song J, Wang G,et al.Spatiotemporal characteristic and forecast of drought in Northern Xinjiang,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2021,127:107712. |
| [47] | Jia Z, Wang X, Feng X,et al.Exploring the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services and influencing factors on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Ecological Indicators,2023,154:110521. |
| [48] | 张春悦,白永平,杨雪荻,等.多情景模拟下宁夏平原生态系统服务簇识别研究[J].地理研究,2022,41(12):3364-3382. |
| [49] | 全江涛,杨永芳,周嘉昕.河南省土地资源承载力时空演变分析与预测[J].水土保持研究,2020,27(2):315-322. |
| [50] | 谢高地,张彩霞,张雷明,等.基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进[J].自然资源学报,2015,30(8):1243-1254. |
| [51] | Zhu W, Gao Y, Zhang H,et al.Optimization of the land use pattern in Horqin Sandy Land by using the CLUMondo model and Bayesian belief network[J].Science of the Total Environment,2020,739:139929. |
| [52] | Xia H, Kong W, Zhou G,et al.Impacts of landscape patterns on water-related ecosystem services under natural restoration in Liaohe River Reserve,China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,792:148290. |
| [53] | Hu Y, Gong J, Li X,et al.Ecological security assessment and ecological management zoning based on ecosystem services in the West Liao River Basin[J].Ecological Engineering,2023,192:106973. |
| [54] | 刘志民,余海滨.“山水林田湖草沙生命共同体”理念下的科尔沁沙地生态治理[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):34-40. |
| [55] | Fan J, Xu Y, Ge H,et al.Vegetation growth variation in relation to topography in Horqin Sandy Land[J].Ecological Indicators,2020,113:106215. |
| [56] | 王彦颖.中国东北植被时空动态变化及其对气候响应研究[D].长春:东北师范大学,2016. |
| [57] | 肖巍.科尔沁沙地南缘退化耕地风沙危害状况[J].江西农业,2019(12):84. |
| [58] | 马浩文,王永芳,郭恩亮.基于GEE的翁牛特旗土地沙漠化遥感监测[J].干旱区研究,2023,40(3):504-516. |
| [59] | 朱梦媛,田一辰,金磊,等.科尔沁沙地南缘生态屏障区防风固沙功能时空变化及其影响因素[J].生态学杂志,2025,44(6):1857-1865. |
| [60] | Pan Z, Gao G, Fu B,et al.Exploring the historical and future spatial interaction relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services in the Yangtze River Basin,China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2023,428:139401. |
| [1] | 王卫国, 谢欢, 冯国庆, 家淑珍. 京津风沙源治理工程区生态环境质量及驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 139-152. |
| [2] | 姚博, 连杰, 龚相文, 牟晓明, 李玉霖, 李玉强, 王旭洋. 科尔沁沙地土壤微生物碳氮磷化学计量空间格局及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 153-165. |
| [3] | 张建鹏, 雷鹿鸣, 李玉强, 李天爱, 赵学勇, 任浩彤, 贾虹, 王洋洋, 崔立晗. 生态系统服务供需视角下科尔沁沙地人地系统可持续性评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 176-189. |
| [4] | 宁志英, 李玉霖, 赵学勇, 张彦军, 王海兵, 闫敏, 刘瑞敏, 左合君. 科尔沁沙地优势植物凋落物分解对土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 190-199. |
| [5] | 刘永杰, 杜鹤强, 范亚伟, 杨胜飞. 基于Google Earth Engine(GEE)的毛乌素沙地风蚀荒漠化过程监测[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 262-274. |
| [6] | 贾虹, 张建鹏, 刘连友, 刘吉夫, 杨思琪. 共和盆地生境质量演变及多情景模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 29-36. |
| [7] | 萨仁高娃, 赵媛媛, 耿鑫智, 王岳, 高广磊. 内蒙古沙区2000—2020年人地系统可持续性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 71-82. |
| [8] | 贾虹, 刘连友, 刘吉夫. 共和盆地土地荒漠化敏感性评估[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 1-9. |
| [9] | 陈兵兵, 盖迎春, 宋忠航, 吴向楠, 艾宇, 杨映, 王生棠, 刘宇烁. 祁连山地区生态质量时空变化及驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 258-267. |
| [10] | 夏鸿华, 杨林山, 冯起, 苏迎庆, 邹星怡, 贺王含. 石羊河流域产水服务供需时空变化及驱动因子[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 87-99. |
| [11] | 张晶, 左小安, 吕朋. 生长季降水格局变化对科尔沁沙地典型生境植物群落结构、功能和地上生物量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 1-13. |
| [12] | 段翰晨, 黄背英. 基于AHP与改进型MEDALUS模型耦合的科尔沁沙地土地沙漠化敏感性综合评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 137-148. |
| [13] | 刘二燕, 赵媛媛, 周蝶, 武海岩, 高广磊, 丁国栋. 科尔沁-浑善达克沙地2000—2020年土地沙化时空变化格局[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 46-56. |
| [14] | 杨华庆, 朱睿, 尹振良, 山建安, 张薇, 方春爽. 2001—2020年黄河流域水源涵养区植被覆盖变化及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 57-70. |
| [15] | 申子傲, 吴静, 李纯斌. 2000—2020年河西内陆河流域植被覆盖时空变化特征及其驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 119-127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
